Glaucoma is a collection of eye disorders that cause damage to the optic nerve, which transmits visual information from the eye to the brain. This injury is frequently caused by increased intraocular pressure (IOP) within the eye.
When the fluid in the eye, known as aqueous humour, does not drain adequately, IOP can build up. This can put additional strain on the optic nerve, causing it to get injured over time. Glaucoma, if left untreated, can lead to permanent visual loss and blindness. Continue reading to learn about the various symptoms of glaucoma and how to prevent it.
1. Changes or loss of vision
Progression of peripheral vision loss is the most typical symptom of glaucoma. Patients may experience blurred vision or a gradual narrowing of their visual field.
2.Tunnel vision
Tunnel vision is a defining feature of advanced glaucoma, in which only a tiny centre area of vision remains clear while peripheral vision is severely damaged.
3. Hazy vision
Glaucoma can cause blurring of vision, which makes it difficult to notice minute details or read letters well.
4. Light haloing or glare
Glaucoma can cause increased sensitivity to light, resulting in halos or glare surrounding light sources, particularly at night.
5. Eye discomfort
Some people may develop eye pain, which can vary from minor discomfort to severe stinging or throbbing pain. This is often accompanied by redness in the affected eye.
6. Vomiting and nausea
Patients suffering from acute angle-closure glaucoma may experience nausea, vomiting, and even abdominal discomfort.
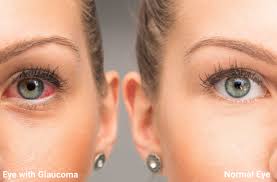
7. Redness of the eyes
Glaucoma-related redness in the eye can occur as a result of elevated pressure or inflammation. Itching or irritation is frequently present.
8. Damage to the optic nerve
Glaucoma causes optic nerve damage, which an ophthalmologist can detect during an eye exam. They may identify weakening of the optic nerve head or changes in its appearance.