Internet Of Things-IOT
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming how we interact with the world, offering unprecedented opportunities for automation, efficiency, and convenience. With applications ranging from smart homes and healthcare to industrial systems, IoT is set to drive major changes across numerous industries and improve the overall quality of life. However, challenges related to security, interoperability, and data management persist. Despite these hurdles, ongoing technological advancements and infrastructure improvements continue to address these issues, and IoT's role in creating an increasingly interconnected and intelligent world remains clear.

The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the interconnected network of physical objects-such as devices, vehicles, appliances, and other items-equipped with sensors, software, and network connectivity that enable them to collect, share, and act on data. IoT's main objective is to create more intelligent environments where devices can interact autonomously, exchange real-time information, and make decisions that improve productivity, convenience, and efficiency. This technology has drastically transformed industries, from healthcare and manufacturing to agriculture and home automation.
Core Components of IoT
1. Devices and Sensors: Central to IoT are the physical objects (devices) integrated with sensors and actuators. These devices collect environmental data such as temperature, motion, humidity, and location. The sensors detect changes and send this data to the cloud or other connected devices for further processing.
2. Connectivity: For IoT devices to communicate effectively, they require a stable network connection. These devices use various communication technologies such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, LTE, and increasingly, 5G. The choice of network is influenced by factors like range, power consumption, and data transfer speed.
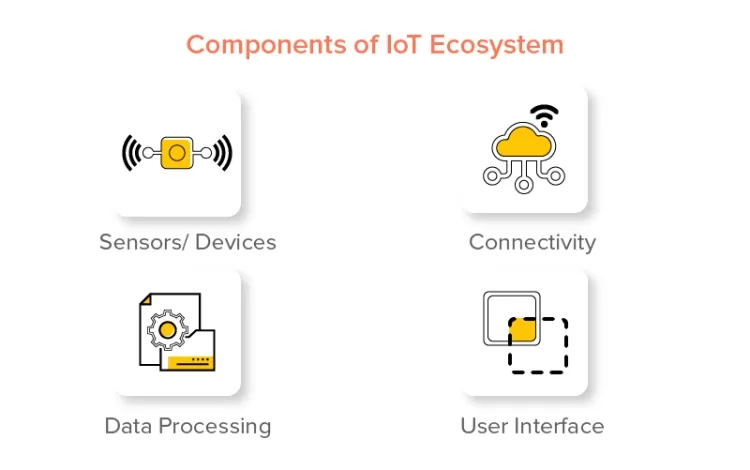
3. Data Processing and Cloud Computing: Data generated by IoT devices must be processed to extract actionable insights. This processing typically occurs in the cloud, where data can be stored, analyzed, and interpreted using tools like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and big data analytics. Cloud computing enables the real-time analysis and storage of vast quantities of data generated by IoT devices.
4. Actuators: These components take action based on the data received. For instance, in a smart thermostat, an actuator might adjust the room temperature based on sensor readings. Actuators control devices like lights, locks, and motors, executing responses as needed.
5. User Interface: The user interface allows individuals to interact with IoT systems. It can take the form of mobile apps, web dashboards, or voice commands, giving users the ability to monitor and control IoT devices remotely.
IoT Applications
IoT's applications span a wide range of areas, impacting both personal and industrial environments. Some key applications include:
1. Smart Homes: IoT has given rise to the concept of the "smart home," where common household devices-such as lights, thermostats, security cameras, and appliances-are connected to the internet. These devices can be controlled remotely via smartphones, voice assistants, or set to function automatically, improving convenience, energy efficiency, and home security.
2. Healthcare and Medical Devices: IoT is revolutionizing healthcare by facilitating remote patient monitoring and real-time data collection. Wearable devices such as fitness trackers, heart rate monitors, and glucose sensors gather critical data and transmit it to healthcare providers for analysis. These devices help doctors offer timely, proactive care by detecting health issues early.
3. Industrial IoT (IIoT): In sectors like manufacturing, IoT is used to enhance productivity, reduce downtime, and increase safety. Sensors embedded in machinery monitor performance, detect faults, and predict maintenance needs, which minimizes unplanned breakdowns and optimizes operations. Additionally, IoT facilitates real-time inventory tracking, supply chain management, and logistics.
4. Smart Cities: IoT plays a vital role in creating smarter cities where urban infrastructure-such as traffic systems, waste management, and energy usage-are interconnected to improve efficiency. For instance, traffic sensors can adjust signal timings based on real-time traffic flow, while waste bins equipped with IoT sensors notify city workers when they need to be emptied.
5. Agriculture: IoT also finds applications in agriculture by assisting farmers with crop management, livestock monitoring, and equipment control. IoT sensors track soil moisture levels, weather conditions, and plant health, enabling optimized irrigation and enhanced crop yields. For livestock management, IoT-enabled collars monitor animal health and behavior, alerting farmers to potential issues.
Benefits of IoT
1. Enhanced Efficiency and Automation: IoT drives automation by enabling devices to interact and make decisions based on real-time data, reducing the need for manual intervention and boosting operational efficiency.
2. Cost Reduction: IoT helps organizations lower costs by optimizing resource usage. In manufacturing, for example, IoT devices can predict when equipment will require maintenance, preventing expensive repairs. Smart homes can also optimize energy usage, lowering utility bills.
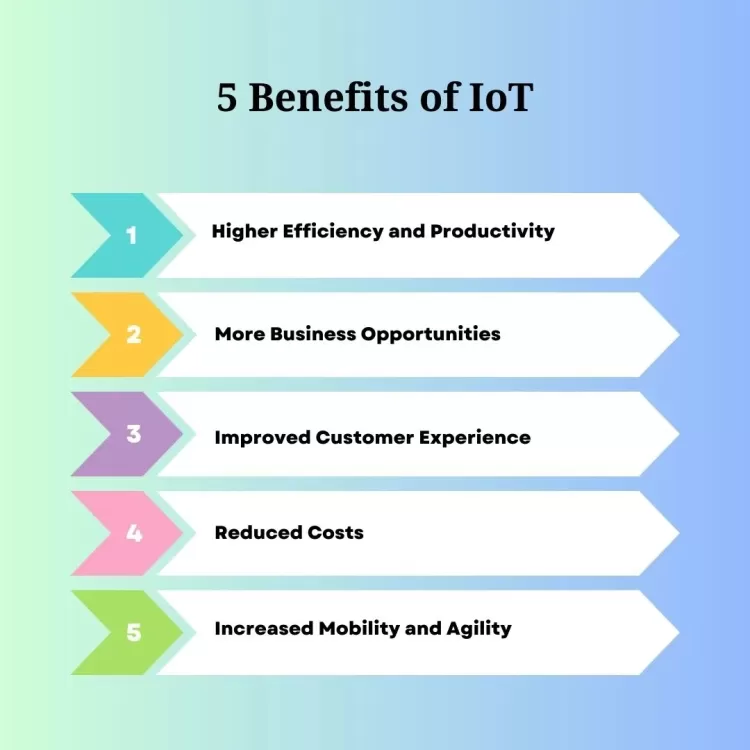
3. Real-Time Data and Decision Making: With IoT, businesses can access real-time data, enabling them to make more informed decisions. This can include tracking inventory, adjusting production rates, or responding to customer behavior promptly.
4. Improved Safety and Security: IoT improves safety and security by providing continuous monitoring and generating alerts. In homes, IoT-based security systems can detect intrusions, while in industrial environments, IoT sensors can detect hazardous conditions, prompting necessary safety actions.
Challenges of IoT
While IoT offers substantial advantages, it also faces several challenges:
1. Security and Privacy: The vast amount of data collected by IoT devices, including sensitive personal information, raises concerns about privacy and cybersecurity. Securing IoT systems requires strong encryption, regular software updates, and robust authentication measures.
2. Interoperability: As the number of IoT devices and platforms continues to grow, ensuring that these devices can communicate seamlessly with each other remains a challenge. Standardizing communication protocols and interfaces is crucial for achieving interoperability.
3. Data Management: IoT devices generate enormous volumes of data that require efficient storage, analysis, and processing. Managing and deriving useful insights from this data is essential for maximizing the potential of IoT applications.
What's Your Reaction?