Veggies: The real superfood.
Vegetables are the foundation of a healthy diet, offering an abundance of essential nutrients, fiber, and antioxidants that support overall health. Whether you enjoy them raw, cooked, or blended into smoothies, incorporating a variety of vegetables into your meals can help prevent disease, manage weight, and boost your energy. With so many delicious options and cooking methods, adding more vegetables to your diet is both simple and rewarding, providing countless health benefits for years to come.
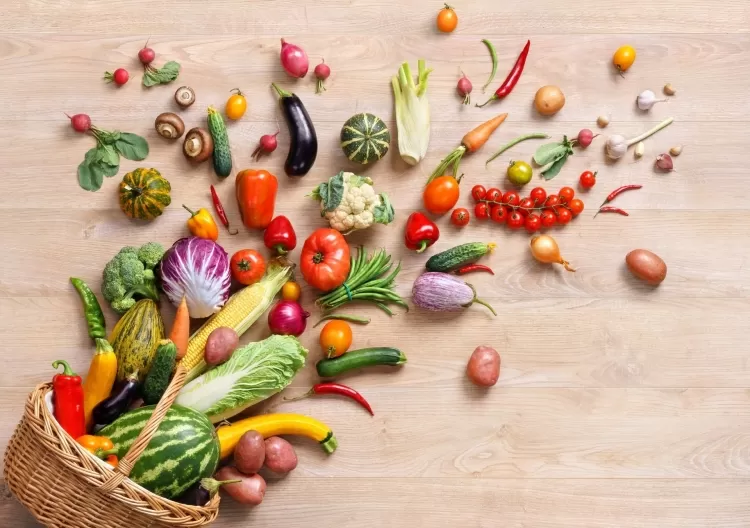

Vegetables play a vital role in maintaining a healthy diet, providing a diverse range of nutrients, flavors, and textures. From leafy greens to root vegetables, these plant-based foods are packed with vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants, all of which promote overall health and wellness. This article will delve into the various types of vegetables, their health benefits, and tips on how to incorporate more of them into your daily meals.
Types of Vegetables
Vegetables come in an impressive array of shapes, sizes, and colors, with each variety offering distinct nutritional advantages. Vegetables can generally be grouped into several categories based on the part of the plant that is consumed:
1.Leafy Greens: This category includes vegetables such as spinach, kale, lettuce, and Swiss chard. Leafy greens are high in vitamins A, C, K, and several B vitamins, as well as essential minerals like iron, calcium, and magnesium. They are also packed with fiber and low in calories, making them excellent for weight management.

2. Cruciferous Vegetables: Members of the cabbage family, such as broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, and cabbage, fall into this group. Known for their cancer-fighting properties due to glucosinolates, cruciferous vegetables are also rich in fiber, vitamin C, and folate.
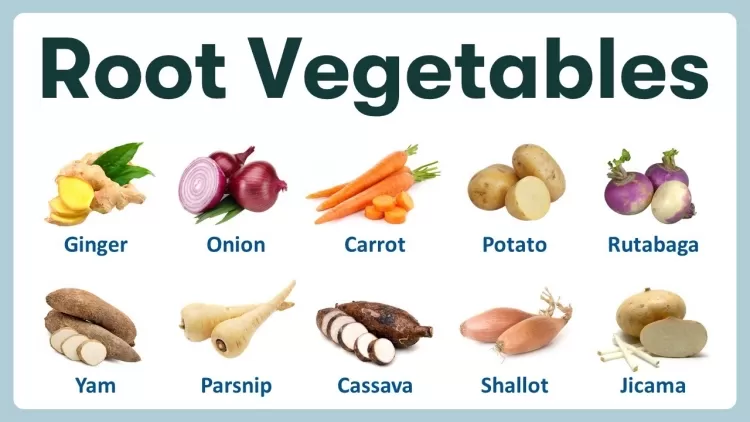
3. Root Vegetables: Root vegetables grow beneath the soil and include carrots, sweet potatoes, beets, and turnips. These starchy vegetables are an excellent source of carbohydrates, providing energy, and they are packed with vitamins and minerals like beta-carotene in carrots and potassium in sweet potatoes.
4. Fruiting Vegetables: Although botanically classified as fruits, vegetables such as tomatoes, cucumbers, bell peppers, and zucchini are commonly considered vegetables in culinary contexts. They are typically rich in vitamins C and A and are hydrating due to their high water content.
5. Allium Vegetables: Garlic, onions, leeks, shallots, and scallions fall into this group. Known for their strong aroma and flavor, allium vegetables contain sulfur compounds that are linked to various health benefits, including supporting heart health and boosting the immune system.
6. Legumes: Although often categorized separately, legumes such as peas, beans, and lentils are technically vegetables. These nutrient-dense foods are a great source of protein, fiber, and essential minerals like iron and magnesium, making them ideal for vegetarians and vegans.
7. Tubers: Tubers, including potatoes and yams, are starchy vegetables that are rich in carbohydrates, fiber, and vitamin C. These versatile vegetables are a hearty base for many meals and can be roasted, mashed, or baked.
8. Mushrooms: Although fungi, mushrooms are typically grouped with vegetables in the kitchen. They are low in calories but high in antioxidants, fiber, and essential nutrients like B vitamins and selenium.
Health Benefits of Vegetables
Eating a wide variety of vegetables provides numerous health advantages. Here are some of the most significant benefits:
1. Packed with Nutrients: Vegetables are a rich source of vital nutrients that support the body’s proper functioning. For example, leafy greens and cruciferous vegetables are full of vitamins and minerals that help strengthen the immune system, promote healthy bones, and maintain glowing skin.
2. High in Fiber: Fiber plays an important role in digestive health, helping to prevent constipation. Vegetables, especially fiber-rich options like broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and carrots, support healthy digestion and contribute to regular bowel movements.
3. Supports Weight Management: Vegetables are naturally low in calories but high in nutrients and fiber, making them an excellent choice for those looking to manage their weight. Fiber increases satiety, reducing hunger and preventing overeating.

4. Rich in Antioxidants: Many vegetables are packed with antioxidants that protect the body from oxidative stress and reduce the risk of chronic conditions such as heart disease, cancer, and diabetes. For example, tomatoes contain lycopene, an antioxidant that has been linked to a lower risk of prostate cancer, while spinach is rich in lutein, which promotes healthy vision.
5. Promotes Heart Health: Vegetables like sweet potatoes and spinach, which are high in potassium, can help regulate blood pressure and improve heart health. Additionally, compounds found in vegetables like flavonoids help reduce inflammation and improve blood vessel function.
6. Boosts Immunity: Vegetables such as bell peppers, kale, and broccoli are high in vitamin C, a nutrient crucial for a strong immune system. Regularly consuming vitamin C-rich vegetables can enhance the body’s ability to fight infections and diseases.
7. Prevents Disease: A vegetable-rich diet has been associated with a lower risk of various chronic diseases, including certain cancers, heart disease, and type 2 diabetes. The antioxidants, fiber, and phytochemicals found in vegetables help protect the body’s cells from damage and reduce inflammation, key factors in disease prevention.
Tips for Adding More Vegetables to Your Diet
Incorporating more vegetables into your meals is simple and enjoyable. Here are some helpful ideas:
1. Start Your Day with Vegetables: Add spinach or kale to your morning smoothie, or sauté mushrooms and onions to include in an omelet or scrambled eggs. This provides a nutrient boost from the very beginning of your day.
2. Snack on Veggies: Keep sliced vegetables like carrots, cucumbers, and bell peppers in the fridge for a quick and healthy snack. Pair them with hummus or a yogurt dip for extra flavor and nutrition.
3. Add Vegetables to Soups and Stews: Enhance the flavor, texture, and nutritional value of soups, stews, and casseroles by adding a variety of vegetables such as carrots, celery, and zucchini.

4. Use Vegetables as Carbohydrate Alternatives: Swap out traditional grains or pasta with cauliflower rice or zucchini noodles (zoodles). This can reduce calorie intake while increasing vegetable consumption.
5. Experiment with New Vegetables: Try vegetables you may not be familiar with, such as artichokes, parsnips, or eggplant. Introducing new vegetables to your meals keeps things interesting and adds different nutritional benefits.
6. Make Vegetables the Main Attraction: Consider making vegetables the star of your meals by preparing a vegetable stir-fry or roasted vegetable platter. This ensures you’re getting a generous serving of vegetables while enjoying a flavorful dish.
What's Your Reaction?

















