The Role of Heart Stents in Treating Coronary Artery Disease...!!!
Heart stents are a vital tool in the treatment of coronary artery disease, helping to restore blood flow and enhance heart function. The procedure is minimally invasive and has a quick recovery time, making it a favored option for many patients.
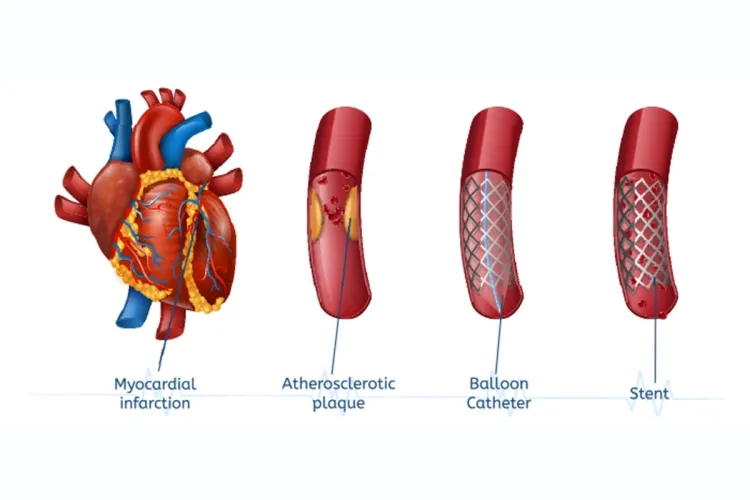
Heart stents are small, expandable tubes used to open narrowed or blocked arteries in the heart, ensuring proper blood flow. The process of placing a heart stent, known as angioplasty, is a common procedure to treat coronary artery disease (CAD).
Preparation for the Procedure
Before a heart stent procedure, your doctor will review your medical history and perform a physical examination. Diagnostic tests such as an electrocardiogram (ECG), stress test, and coronary angiography may be conducted to assess the severity of the blockage and plan the procedure.
The Procedure
-
Anesthesia: The procedure typically involves local anesthesia to numb the area where the catheter will be inserted (usually the groin, arm, or wrist). In some cases, general anesthesia may be used.
-
Catheter Insertion: A thin, flexible catheter is inserted into a blood vessel in the groin, arm, or wrist and guided to the blocked coronary artery using imaging techniques.
-
Balloon Angioplasty: Once the catheter reaches the blockage, a small balloon at the tip is inflated to open up the artery, restoring blood flow to the heart muscle.
-
Stent Placement: After the artery is widened, a stent (a small wire mesh tube) is placed at the site of the blockage. The stent is expanded using the balloon, which is then deflated and removed, leaving the stent in place to keep the artery open.
-
Post-Procedure Care: After the procedure, the catheter site is closed, and you'll be monitored for any complications. A short hospital stay for observation may be necessary.
Recovery and Follow-Up
Recovery from a heart stent procedure is usually swift. Most patients can resume normal activities within a few days. However, it's important to follow your doctor's instructions regarding medications, lifestyle changes, and follow-up appointments to ensure the best outcome.
Risks and Complications
While heart stent procedures are generally safe, some risks include bleeding at the catheter insertion site, blood clots, and artery damage. Your doctor will discuss these risks with you and take steps to minimize them.
Benefits of Heart Stents
Heart stents can significantly improve blood flow to the heart, relieve symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath, and reduce the risk of heart attacks. They are an invaluable treatment option for patients with coronary artery disease.
Heart stents are a vital tool in the treatment of coronary artery disease, helping to restore blood flow and enhance heart function. The procedure is minimally invasive and has a quick recovery time, making it a favored option for many patients. If you have any concerns or questions about the procedure, it's important to discuss them with your doctor to ensure you receive the best care possible.
What's Your Reaction?