Latitude and Longitude: The Backbone of Geographic Navigation...!!!
Latitude and longitude enable us to pinpoint any location on the planet and play a pivotal role in navigation, mapping, and various scientific fields.
Latitude and Longitude: An In-Depth Exploration
Latitude and Longitude: An Introduction
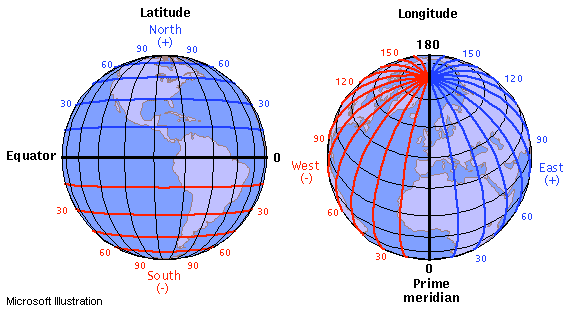
Latitude and longitude comprise a geographic coordinate system that enables precise identification of any location on Earth’s surface. This system creates a grid over the globe using imaginary lines called parallels (latitude) and meridians (longitude).
Latitude: The Horizontal Lines
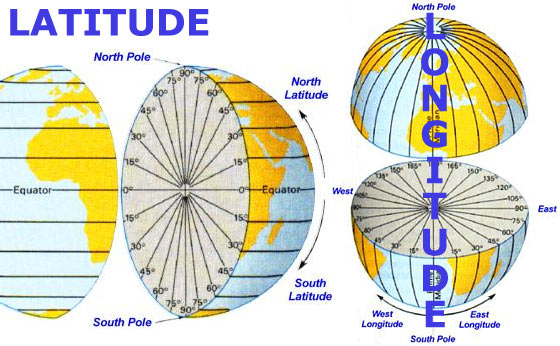
Latitude measures the distance north or south of the Equator, expressed in degrees (°), minutes ('), and seconds ("). The Equator is designated as 0° latitude. Latitude lines, or parallels, run horizontally around the Earth, parallel to the Equator, and range from 0° at the Equator to 90° at the poles, with the North Pole at 90°N and the South Pole at 90°S.
Latitude lines are crucial in determining regional climate and weather patterns. For instance, areas at higher latitudes (closer to the poles) experience colder climates, while regions near the Equator enjoy warmer, more stable temperatures.
Longitude: The Vertical Lines
Longitude measures the distance east or west of the Prime Meridian, set at 0° longitude and passing through Greenwich, England. Similar to latitude, longitude is expressed in degrees, minutes, and seconds. Longitude lines, or meridians, run vertically from the North Pole to the South Pole. They range from 0° at the Prime Meridian to 180° at the International Date Line in both the eastern and western hemispheres.
Unlike latitude lines, longitude lines converge at the poles, causing the distance between meridians to vary based on latitude. At the Equator, the distance between each degree of longitude is about 111 kilometers (69 miles), but this distance decreases toward the poles.
Intersection of Latitude and Longitude
The exact position of any point on Earth’s surface is identified by the intersection of a latitude and longitude line, often referred to as geographic coordinates. These coordinates are typically written in degrees, minutes, and seconds, such as 40°44'55"N, 73°59'11"W for New York City.
Importance in Navigation and Mapping
Latitude and longitude are vital for navigation, helping explorers, sailors, and pilots determine their precise location globally. Before modern technology, early navigators relied on celestial navigation, using stars, the sun, and the moon alongside these coordinates to chart their paths.
Today, latitude and longitude are fundamental to the Global Positioning System (GPS), used worldwide for navigation. GPS devices receive satellite signals to calculate the user’s exact location in terms of latitude and longitude. This technology is crucial for everything from driving directions and aviation to outdoor activities and scientific research.
Historical Background and Evolution
The idea of a geographic coordinate system has ancient roots. Greek mathematicians like Ptolemy made significant contributions to early cartography and the development of latitude and longitude. The system we use today was further refined during the Age of Exploration, when accurate navigation became essential for global exploration and trade.
The Prime Meridian’s establishment at Greenwich in 1884 standardized global navigation, ensuring consistent and accurate mapping. This international agreement also addressed timekeeping and the calculation of time zones, as longitude is closely linked to measuring time.
Applications Across Various Domains
Beyond navigation, latitude and longitude have numerous applications. They are critical for geographic information systems (GIS), which are used in urban planning, environmental conservation, disaster management, and more. Scientists employ these coordinates to study climate patterns, animal migrations, and geological phenomena. Additionally, latitude and longitude are fundamental in aviation, guiding flight paths and ensuring safety.
Latitude and longitude are essential components of our understanding of Earth’s geography. They enable us to pinpoint any location on the planet and play a pivotal role in navigation, mapping, and various scientific fields. From ancient explorers to modern GPS technology, these coordinates continue to be indispensable tools in our quest to comprehend and traverse the world
What's Your Reaction?