FlexMotion: Advancing Human Motion Generation with Efficiency and Control
Human motion synthesis has gained prominence across fields like animation, virtual reality (VR), robotics, and human-computer interaction (HCI). As technology evolves, the need for lightweight, physically plausible, and controllable models becomes crucial. Existing methods for motion generation often face trade-offs between computational efficiency, physical realism, and control over motion parameters. FlexMotion is a groundbreaking framework designed to overcome these limitations, providing a solution that ensures realistic motion generation, enhances computational efficiency, and offers fine-grained control over spatial parameters.
The Challenge of Generating Human Motion
Generating realistic and controllable human motion is complex due to the intricate interactions between joint movements, contact forces, and muscle activations. These dynamics require models that can balance kinematics (the study of motion) and dynamics (the study of forces and their effect on motion). Traditional models often fall short of handling this balance efficiently. For instance, methods that focus solely on physical plausibility tend to require high computational resources, often using physics engines, making them impractical for real-time applications. Additionally, many existing models lack the capability to control specific aspects of human motion, like joint actuation or muscle activation, which are vital in areas such as sports, rehabilitation, and robotics.
Introducing FlexMotion: A Lightweight, Physics-Aware Framework
FlexMotion is a novel framework that generates human motion sequences by integrating physical plausibility, computational efficiency, and spatial controllability. Unlike traditional models that rely on complex physics simulators, FlexMotion operates efficiently in the latent space, making it lightweight and fast to train and infer.
Key Features of FlexMotion
-
Multimodal Pre-Trained Transformer Model: FlexMotion utilizes a Transformer encoder-decoder model that integrates multiple types of input data, including joint locations, contact forces, joint actuation, and muscle activations. This allows the model to generate human motion that is not only realistic but also physically plausible, ensuring alignment with human biomechanics.
-
Plug-and-Play Spatial Control Module: One of the standout features of FlexMotion is its ability to provide spatial control over motion parameters. This plug-and-play module allows users to control a range of parameters, such as joint locations, muscle activations, joint actuation, and contact forces. This level of control ensures that the generated motions meet specific needs, such as precise trajectories or muscle activations, making the framework adaptable to various domains.
-
Efficient Diffusion Model: FlexMotion operates with a diffusion model that works in the latent space, drastically reducing the computational cost for training and inference. The model generates human motion by applying a lightweight and efficient denoising diffusion probabilistic model (DDPM). Unlike traditional methods that rely on physics simulators, the diffusion approach makes FlexMotion faster and more computationally efficient, without compromising the quality or physical realism of the generated motions.
Capabilities and Use Cases
FlexMotion’s ability to generate physically plausible human motion with spatial control is demonstrated through several examples:
-
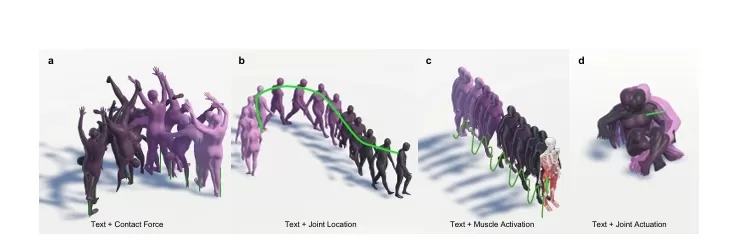
Hands Spring with Contact Forces: In this case, the model generates a human handspring by considering contact forces as part of the input. The generated motion adheres to the physical constraints of the human body, ensuring that the interaction with the ground is realistic.
-
Walking on a Wavy Path with Spatial Control: By controlling the spatial parameters, the model generates a walking motion where the trajectory follows a wavy path. This demonstrates FlexMotion’s ability to generate motion with specific spatial constraints.
-
Walking with Muscle Activation Control: FlexMotion can also generate motion by controlling muscle activations. For instance, the model can simulate walking using quadriceps activation over time, allowing precise control over the muscle contributions to the walking pattern.
-
Hand Movement with Joint Actuation Control: In another example, the model generates a hand movement while the user sits on the ground, controlled by joint actuation and text descriptions, demonstrating the flexibility and adaptability of the system.
These examples highlight the range of motions FlexMotion can generate, from dynamic actions like handsprings to precise, controlled movements like walking or hand gestures.
Advantages of FlexMotion
1. Physical Plausibility
FlexMotion is the first method to ensure that the generated motions adhere to physical constraints by integrating muscle activations, joint actuations, and contact forces into the learning process. This multimodal approach ensures that the generated motion sequences are not just plausible but also accurately reflect the biomechanics of human movement.
2. Computational Efficiency
By operating in the latent space and using a diffusion model, FlexMotion significantly reduces the computational overhead compared to traditional methods that require complex physics simulations. This enables faster training and inference, making it suitable for real-time applications.
3. Enhanced Controllability
FlexMotion provides a plug-and-play control module that allows users to manipulate spatial parameters such as joint locations, muscle activations, and contact forces. This level of control is crucial in applications like robotics, virtual reality, and rehabilitation, where fine-grained control over human-like motion is essential.
Experimental Validation
FlexMotion has been evaluated on multiple popular datasets, including HumanML3D, KIT-ML, and FLAG3D. In these experiments, FlexMotion demonstrated superior performance in terms of:
- Realism: The generated motions are highly realistic and maintain fidelity to human biomechanics.
- Physical Plausibility: The model adheres to the physical constraints of human movement, making the generated motions not only realistic but also plausible in a real-world context.
- Controllability: FlexMotion excels in providing users with the ability to control the motion along various parameters, enhancing its utility in diverse applications.
Conclusion
FlexMotion sets a new benchmark in human motion synthesis by integrating physical plausibility, computational efficiency, and spatial controllability into a single framework. By operating in the latent space with a diffusion model and offering fine-grained control over various motion parameters, FlexMotion provides a powerful and efficient solution for generating realistic human motion. Whether for robotics, virtual reality, or rehabilitation, FlexMotion’s versatile capabilities open up new possibilities in human motion generation.
What do you think are the most promising applications of FlexMotion in industries like robotics or virtual reality? How do you see this technology evolving in the future?
What's Your Reaction?

















