Building and Utilizing Railway Tracks...!!!
Constructing railway tracks is a complex and meticulous process that ensures the safe and efficient operation of trains. Once built, these tracks serve multiple purposes, from transporting passengers and goods to supporting urban transit and tourism.
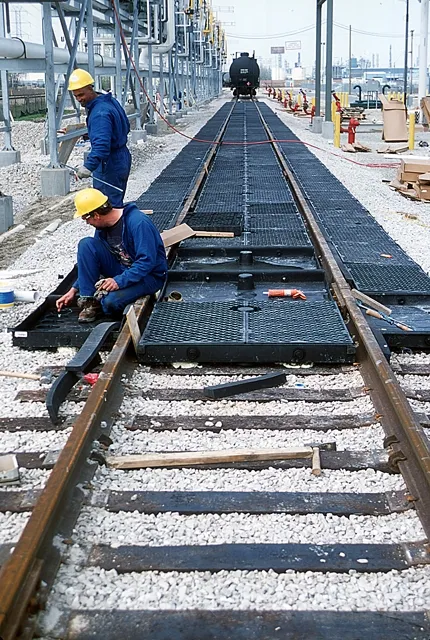

Railway tracks are essential for rail transport, serving as the foundation for train operations. Constructing railway tracks involves a meticulous and detailed process to ensure safety, durability, and efficiency. Once completed, these tracks fulfill various roles, from transporting goods to facilitating passenger travel.
Construction of Railway Tracks
-
Survey and Planning:
-
The process begins with a comprehensive survey and planning phase. Engineers conduct topographical surveys to identify the optimal route, considering factors such as terrain, gradients, and curves. The aim is to minimize construction costs and ensure the railway line's safety and efficiency.
-
-
Clearing and Excavation:
-
Once the route is finalized, the land is cleared of vegetation, debris, and obstacles. Excavation involves removing soil and rock to create a level surface for the tracks. Tunnels and bridges may be constructed to navigate challenging terrain.
-
-
Subgrade Preparation:
-
The subgrade is the foundational layer beneath the tracks. It must be stable and well-compacted to support the trains' weight and prevent settlement. Materials like gravel, sand, and compacted earth are commonly used to create a solid subgrade.
-
-
Ballast Layer:
-
The ballast layer consists of crushed stone or gravel placed on top of the subgrade. This layer provides stability, drainage, and support for the tracks. It also helps distribute the train load evenly and absorbs vibrations from passing trains.
-
-
Laying the Sleepers (Ties):
-
Sleepers, or ties, are horizontal supports placed on the ballast layer. They can be made of wood, concrete, or steel. Sleepers maintain the correct gauge (distance between the rails) and distribute the load from the rails to the ballast.
-
-
Installing the Rails:
-
Rails are the steel tracks on which trains run. They are laid on top of the sleepers and secured with fasteners like spikes, clips, or bolts. Rails are typically made from high-quality steel to withstand heavy loads and stresses. The ends of the rails are joined using fishplates or welds to create a continuous track.
-
-
Alignment and Leveling:
-
Proper alignment and leveling of the tracks are crucial for safe and smooth train operations. Engineers use specialized equipment to check the alignment and adjust the rails and sleepers as needed. This ensures that the tracks are straight, level, and free from irregularities.
-
-
Final Inspection and Testing:
-
Before the tracks are opened for use, a thorough inspection and testing phase is conducted. This includes checking the integrity of the track components, verifying the gauge and alignment, and testing the track under load conditions. Any issues identified during this phase are addressed to ensure the tracks' safety and reliability.
-

Uses of Railway Tracks
-
Passenger Transport:
-
Railway tracks facilitate the movement of passengers over long and short distances. Trains offer a reliable and efficient mode of transportation for daily commuters, long-distance travelers, and tourists. High-speed rail networks further enhance rail travel by significantly reducing travel times.
-
-
Freight Transport:
-
Railways are a vital mode of transport for goods and commodities. They provide a cost-effective and efficient means of transporting bulk materials, such as coal, minerals, grain, and containers. Rail freight is particularly advantageous for long-distance and heavy cargo, reducing road congestion and carbon emissions.
-
-
Urban Transit:
-
In urban areas, railway tracks support metro and light rail systems, providing an efficient and eco-friendly mode of public transportation. These systems help reduce traffic congestion, lower pollution levels, and improve the overall quality of life for city residents.
-
-
Tourism:
-
Scenic train routes and heritage railways attract tourists, offering a unique and nostalgic travel experience. These journeys often showcase breathtaking landscapes and historical landmarks, contributing to local tourism and the economy.
-
-
Military and Emergency Use:
-
Railway tracks play a crucial role in military logistics, enabling the rapid movement of troops, equipment, and supplies. Additionally, railways can be used during emergencies and natural disasters to transport relief materials and evacuate affected populations.
-
-
Economic Development:
-
Railways contribute to economic development by connecting regions, facilitating trade, and promoting industrial growth. Developing railway infrastructure can lead to job creation, improved market access, and increased economic activity.
-
Constructing railway tracks is a complex and meticulous process that ensures the safe and efficient operation of trains. Once built, these tracks serve multiple purposes, from transporting passengers and goods to supporting urban transit and tourism. By understanding the process of building railway tracks and their diverse uses, we can appreciate their critical role in modern transportation and economic development.
What's Your Reaction?