Understanding Piles: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments...!!!
Piles are a common condition that can cause significant discomfort but are usually manageable with proper treatment and preventive measures.
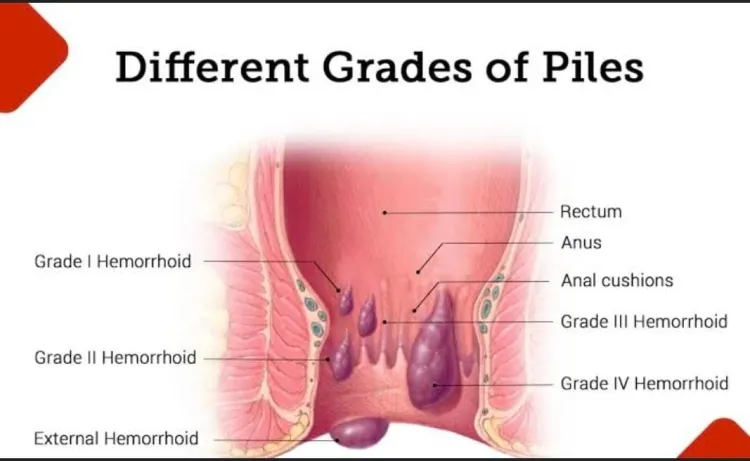
Hemorrhoids, commonly known as piles, are swollen veins found in the lower part of the rectum and anus. This condition can be quite uncomfortable and sometimes painful. Hemorrhoids may form inside the rectum (internal hemorrhoids) or under the skin surrounding the anus (external hemorrhoids). In some instances, both internal and external hemorrhoids can occur together, leading to a more severe condition.
Causes of Piles
Piles result from increased pressure in the lower rectum, which can be caused by several factors:
-
Straining during bowel movements: Often due to chronic constipation or diarrhea.
-
Prolonged sitting: Especially when on the toilet.
-
Obesity: Extra weight can add pressure to the veins in the rectal area.
-
Pregnancy: The weight of the fetus and hormonal changes can cause veins to enlarge.
-
Heavy lifting: Frequent lifting of heavy objects can also be a contributing factor.
-
Anal intercourse: This can lead to new hemorrhoids or exacerbate existing ones.
Symptoms
The symptoms of piles vary depending on their type (internal or external) and severity. Common symptoms include:
-
Bleeding during bowel movements: One of the most frequent signs, ranging from mild to severe.
-
Itching or irritation: Around the anal area.
-
Pain or discomfort: This may occur during bowel movements or while sitting.
-
Swelling: Around the anus, which can be tender to the touch.
-
A lump near the anus: Which may be sensitive or painful (more common with external hemorrhoids).

Diagnosis
Diagnosing hemorrhoids involves a physical examination, and sometimes additional tests are required. These can include:
-
Digital rectal examination (DRE): A doctor inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to check for abnormalities.
-
Anoscopy: A scope is used to inspect the lining of the anus and rectum.
-
Sigmoidoscopy: This test uses a flexible tube with a light to examine the lower part of the colon.
-
Colonoscopy: If other conditions are a concern, a full examination of the colon may be necessary.
Treatment Options
Treatment for piles depends on their severity. Common treatments include:
-
Home remedies: Over-the-counter creams, ointments, or pads containing hydrocortisone or witch hazel can provide relief.
-
Warm baths: Soaking in a warm tub for 10-15 minutes several times a day can reduce symptoms.
-
Stool softeners: These can ease the strain during bowel movements.
-
Dietary changes: Consuming high-fiber foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can soften stools and make them easier to pass.
-
Medical procedures: If home remedies are ineffective, medical procedures such as rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, or infrared coagulation may be recommended.
-
Surgery: In severe cases, a hemorrhoidectomy (surgical removal of hemorrhoids) may be necessary.
Prevention
Preventing piles involves maintaining healthy bowel habits and making lifestyle changes. Key prevention strategies include:
-
High-fiber diet: Eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to keep stools soft.
-
Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water to help prevent constipation.
-
Avoiding straining: During bowel movements and using the restroom as soon as the urge occurs.
-
Regular exercise: To prevent constipation and reduce pressure on veins.
-
Maintaining a healthy weight: To lessen the strain on rectal veins.
Piles are a common condition that can cause significant discomfort but are usually manageable with proper treatment and preventive measures. If symptoms persist or worsen, it's essential to seek medical advice to rule out other potential conditions and receive appropriate care. Remember, adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can go a long way in preventing hemorrhoids and maintaining overall well-being.
What's Your Reaction?

















