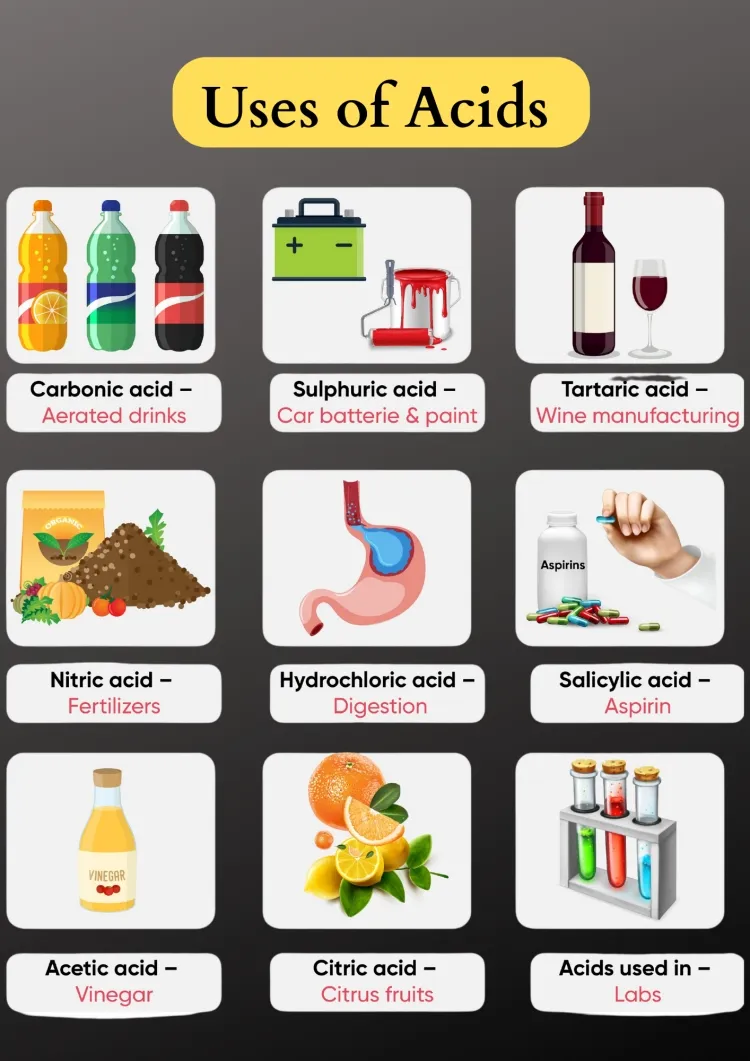
Types of Acids and Their Uses...!!!
Acids are crucial in various industries and everyday applications. From strong acids like hydrochloric and sulfuric acids used in manufacturing and cleaning, to weaker acids like citric and ascorbic acids found in foods and cosmetics, each type of acid has unique properties and uses.
1. Hydrochloric Acid (HCl)
-
Nature: Hydrochloric acid is a strong, corrosive acid typically found in a clear, colorless solution.
-
Uses:
-
Industrial Applications: Utilized in producing chlorides, fertilizers, and dyes.
-
Cleaning Agent: Commonly employed to clean metal surfaces and remove rust.
-
Food Industry: Used in sugar processing and gelatin production.
-
Laboratories: Applied as a reagent in chemical analysis.
-

2. Sulfuric Acid (H₂SO₄)
-
Nature: Sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive, oily liquid that ranges from colorless to slightly yellow.
-
Uses:
-
Manufacturing: A key ingredient in producing fertilizers, particularly phosphate fertilizers.
-
Petroleum Refining: Utilized in refining oil and removing impurities.
-
Battery Acid: Essential for lead-acid batteries in cars and other vehicles.
-
Chemical Synthesis: Used in producing other chemicals, such as hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, and sulfate salts.
-
3. Nitric Acid (HNO₃)
-
Nature: Nitric acid is a highly corrosive, colorless liquid that can cause severe burns.
-
Uses:
-
Fertilizers: Vital in manufacturing ammonium nitrate, a key component of fertilizers.
-
Explosives: Used in producing explosives like nitroglycerin and TNT (trinitrotoluene).
-
Metal Processing: Employed in etching and cleaning metals.
-
Laboratory Reagent: Used for chemical analysis and synthesis in laboratories.
-
4. Acetic Acid (CH₃COOH)
-
Nature: Acetic acid is a colorless liquid with a pungent smell, commonly known as vinegar.
-
Uses:
-
Food Industry: Employed as a preservative and flavoring agent in foods like pickles and sauces.
-
Chemical Industry: Used in producing synthetic fibers, plastics, and rubber.
-
Pharmaceuticals: Utilized in producing various medications.
-
Household: Commonly used as a cleaning agent and for its antibacterial properties.
-
5. Citric Acid (C₆H₈O₇)
-
Nature: Citric acid is a weak, organic acid naturally found in citrus fruits.
-
Uses:
-
Food and Beverages: Employed as a flavoring and preserving agent in foods and drinks.
-
Pharmaceuticals: Used as an acidulant in medications and supplements.
-
Cosmetics: Incorporated in skincare products for its antioxidant properties.
-
Cleaning Agents: Used in cleaning products for its ability to remove stains and limescale.
-

6. Formic Acid (HCOOH)
-
Nature: Formic acid is a colorless, pungent liquid that occurs naturally in some insects.
-
Uses:
-
Agriculture: Used as a preservative and antibacterial agent in livestock feed.
-
Textile Industry: Employed in dyeing and finishing textiles.
-
Leather Industry: Used in tanning and processing leather.
-
Chemical Synthesis: Utilized as an intermediate in various chemical reactions.
-
7. Phosphoric Acid (H₃PO₄)
-
Nature: Phosphoric acid is a clear, colorless liquid or crystalline solid.
-
Uses:
-
Fertilizers: Widely used in producing phosphate fertilizers.
-
Food Industry: Added to soft drinks and processed foods for its tangy flavor.
-
Dentistry: Used in dental cements and as an etching solution in orthodontics.
-
Rust Removal: Employed in rust removers and metal cleaners.
-
8. Ascorbic Acid (C₆H₈O₆)
-
Nature: Ascorbic acid, commonly known as Vitamin C, is a naturally occurring organic compound with antioxidant properties.
-
Uses:
-
Dietary Supplement: Essential nutrient for preventing scurvy and boosting the immune system.
-
Food Industry: Used as a preservative and antioxidant in food products.
-
Cosmetics: Incorporated in skincare products for its anti-aging and brightening effects.
-
Pharmaceuticals: Used in various medicinal formulations for its health benefits.
-
Acids are crucial in various industries and everyday applications. From strong acids like hydrochloric and sulfuric acids used in manufacturing and cleaning, to weaker acids like citric and ascorbic acids found in foods and cosmetics, each type of acid has unique properties and uses. Understanding these acids and their applications helps us appreciate their significance in both industrial processes and daily life.
What's Your Reaction?