The Periodic Table: An Icon of Scientific Progress and Innovation...!!!
The periodic table is a remarkable achievement in the field of science, representing the culmination of centuries of research and discovery.

Introduction: The periodic table is a systematic arrangement of chemical elements, organized according to their atomic number, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. It acts as an essential framework for understanding the relationships between elements and predicting their behavior in chemical reactions. The modern periodic table has developed over time, with contributions from numerous scientists, notably Dmitri Mendeleev, who is often credited with its creation.
Historical Background: The systematic organization of elements began in the early 19th century. In 1869, Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev introduced the first recognizable periodic table, arranging elements by increasing atomic mass and grouping them based on similar properties. Mendeleev's table included gaps, which he predicted would be filled by yet-to-be-discovered elements. His predictions were confirmed with the discovery of elements like gallium and germanium. The periodic table has undergone several refinements since Mendeleev's time, with a significant change being the reorganization of elements based on atomic number rather than atomic mass, as proposed by Henry Moseley in 1913.
Structure and Organization: The periodic table is divided into rows called periods and columns called groups or families. Elements within the same group exhibit similar chemical and physical properties due to having the same number of valence electrons. The table consists of 18 groups and 7 periods, with elements ranging from hydrogen (atomic number 1) to oganesson (atomic number 118).
Periods: Each period corresponds to the highest principal energy level of an element's electrons. Moving from left to right across a period, elements transition from metals to metalloids to nonmetals. For instance, Period 2 includes elements like lithium (metal), boron (metalloid), and fluorine (nonmetal).
Groups:Groups are numbered 1 to 18 and contain elements with similar properties. Notable groups include:
-Group 1: Alkali metals (e.g., lithium, sodium)
-Group 2: Alkaline earth metals (e.g., magnesium, calcium)
-Group 17: Halogens (e.g., chlorine, iodine)
-Group 18: Noble gases (e.g., neon, argon)
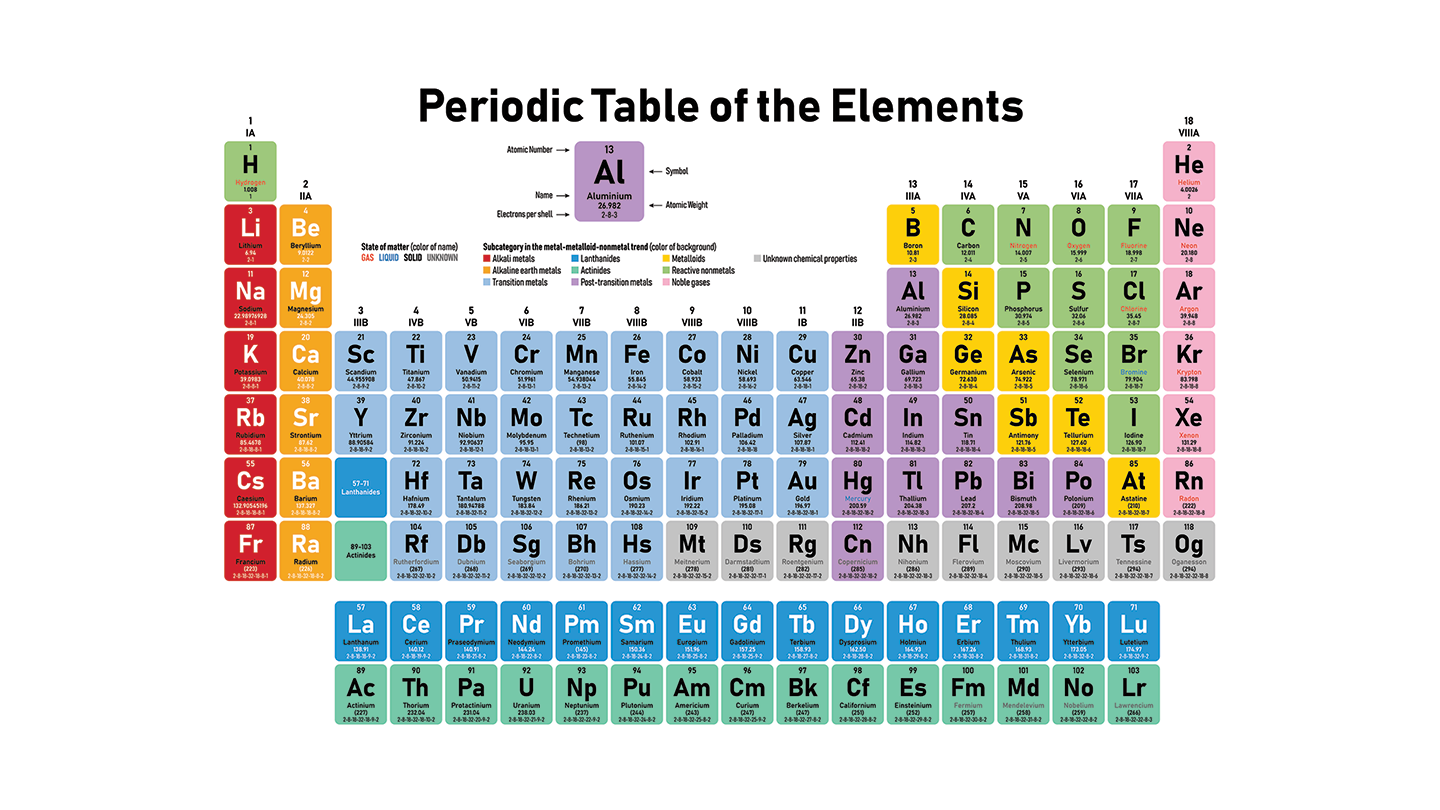
Special Blocks: The periodic table is also divided into blocks based on the subshell in which the last electron resides. These blocks are:
-s-block: Includes Groups 1 and 2, plus hydrogen and helium. These elements have their outermost electron in an s orbital.
-p-block: Includes Groups 13 to 18. Elements in this block have their outermost electron in a p orbital.
-d-block: Includes Groups 3 to 12, also known as transition metals. These elements have their outermost electron in a d orbital.
-f-block: Includes the lanthanides and actinides, which are placed separately at the bottom of the table. These elements have their outermost electron in an f orbital.
Periodic Trends: The periodic table reveals several trends in elemental properties, including atomic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity, and electronegativity.
Atomic Radius: Generally decreases across a period and increases down a group. This is due to the increasing positive charge of the nucleus, which pulls electrons closer.
Ionization Energy: The energy required to remove an electron from an atom. It generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.
Electron Affinity: The energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a neutral atom. It generally becomes more negative across a period and less negative down a group.
Electronegativity: A measure of an atom's ability to attract and bond with electrons. It increases across a period and decreases down a group.
Applications and Significance: The periodic table is a fundamental tool in chemistry, physics, and other sciences. It allows scientists to predict the properties and behaviors of elements and compounds, aiding in the discovery of new materials and the development of new technologies. The periodic table also plays a crucial role in education, providing a visual representation of the relationships between elements.
The periodic table is a remarkable achievement in the field of science, representing the culmination of centuries of research and discovery. Its organization and periodic trends provide invaluable insights into the behavior of elements, making it an essential tool for scientists and students alike. As new elements are discovered and our understanding of atomic structure advances, the periodic table will continue to evolve, reflecting the ever-expanding knowledge of the chemical world.
What's Your Reaction?

















