The Essence of Photosynthesis: Fueling Life on Earth...!!!
Photosynthesis is a crucial biological process that enables plants, algae, and certain bacteria to transform light energy into chemical energy. This process is vital for the survival of most life forms on Earth, as it serves as the primary source of energy and organic matter for nearly all living organisms. Additionally, photosynthesis plays an essential role in maintaining the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Let's dive into the details of photosynthesis, its stages, and its importance.
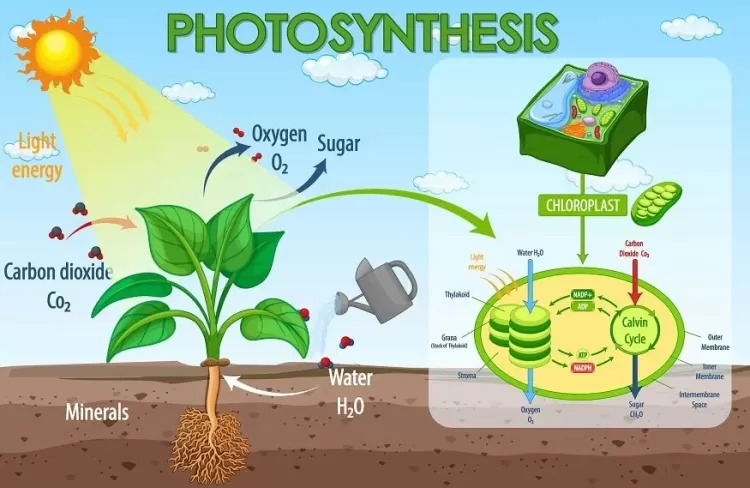
The Basics of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts of plant cells, which contain the pigment chlorophyll. This pigment absorbs light energy, primarily from the blue and red wavelengths, and converts it into chemical energy. The overall equation for photosynthesis can be represented as follows:
In this equation, carbon dioxide () and water () are converted into glucose () and oxygen () using light energy.
The Two Stages of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis consists of two main stages: light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle.
-
Light-Dependent Reactions: These reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts. During this stage, chlorophyll absorbs light energy, which excites electrons and initiates a series of reactions. The primary steps in the light-dependent reactions are:
-
Photolysis of Water: Light energy splits water molecules into oxygen, protons, and electrons. The oxygen is released as a byproduct, while the protons and electrons are used in subsequent reactions.
-
Electron Transport Chain: Excited electrons are transferred through a series of proteins in the thylakoid membrane, creating a flow of electrons. This process generates a proton gradient across the membrane, which is used to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through chemiosmosis.
-
NADP+ Reduction: The electrons eventually reduce nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP+) to form NADPH, a high-energy electron carrier.
The primary products of the light-dependent reactions are ATP and NADPH, which provide the energy and reducing power needed for the next stage of photosynthesis.
-
-
Calvin Cycle (Light-Independent Reactions): The Calvin cycle takes place in the stroma of the chloroplasts. This stage does not require light and uses the ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reactions to convert carbon dioxide into glucose. The main steps in the Calvin cycle are:
-
Carbon Fixation: The enzyme ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO) catalyzes the fixation of carbon dioxide to ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP), forming an unstable six-carbon compound that immediately splits into two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA).
-
Reduction Phase: ATP and NADPH are used to convert 3-PGA into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P), a three-carbon sugar.
-
Regeneration of RuBP: Some G3P molecules are used to regenerate RuBP, allowing the cycle to continue. The remaining G3P molecules are used to synthesize glucose and other carbohydrates.
-
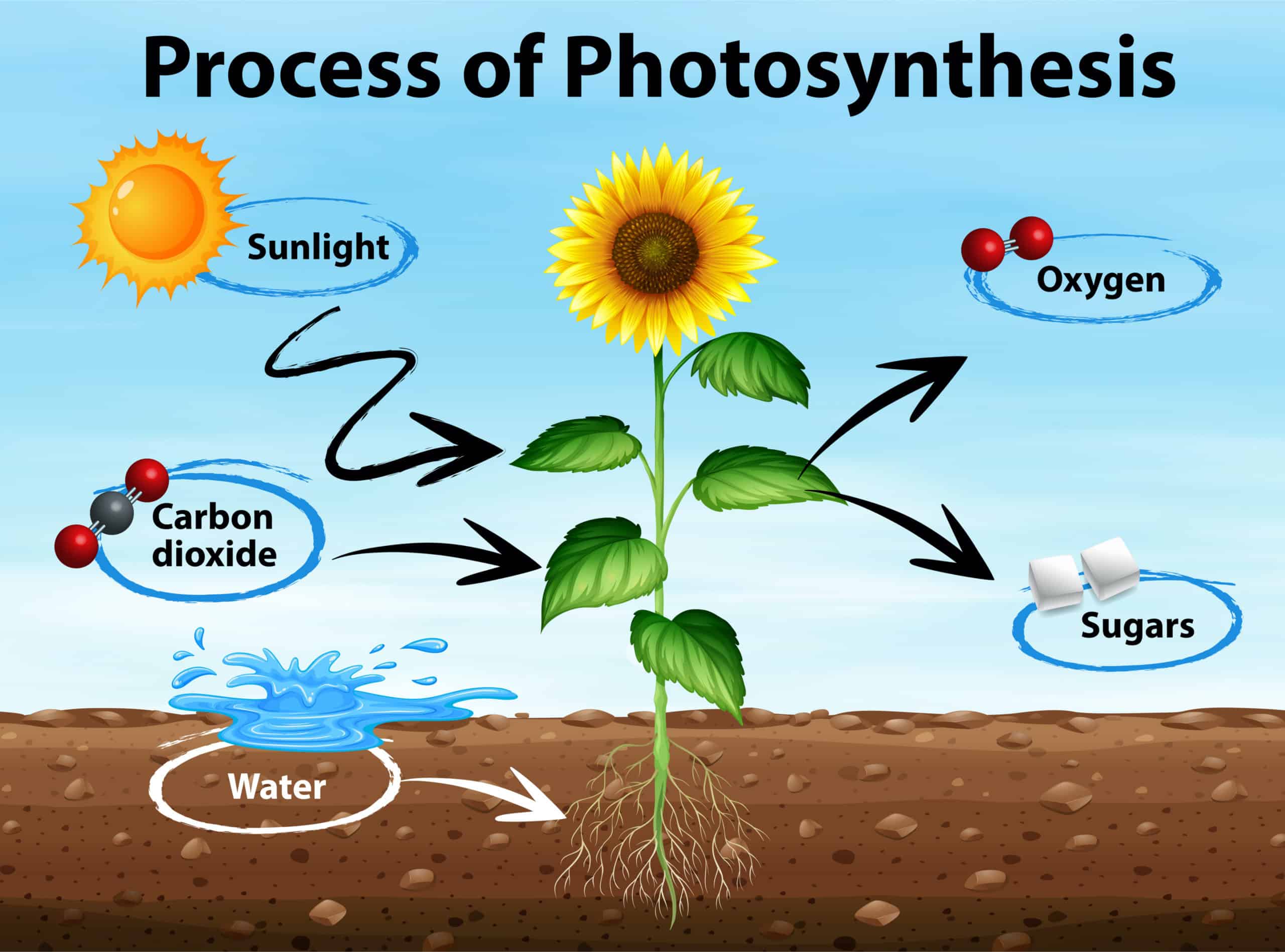
The Significance of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a vital process for several reasons:
-
Energy Production: Photosynthesis provides the primary source of energy for nearly all living organisms. The glucose produced during photosynthesis is used as a fuel for cellular respiration, which generates ATP, the energy currency of cells.
-
Oxygen Production: Photosynthesis is the primary source of atmospheric oxygen. The oxygen released during the light-dependent reactions is essential for the survival of aerobic organisms, including humans.
-
Carbon Dioxide Reduction: Photosynthesis helps regulate the levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Plants absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, reducing the concentration of this greenhouse gas and mitigating its impact on global warming.
-
Foundation of Food Chains: Photosynthetic organisms, also known as autotrophs, form the base of most food chains. They produce organic matter that is consumed by heterotrophs, including herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores.
Photosynthesis is a remarkable and complex process that sustains life on Earth. By converting light energy into chemical energy, photosynthetic organisms provide the essential energy and organic matter needed by nearly all living organisms. Understanding the intricacies of photosynthesis allows us to appreciate its significance in maintaining the balance of life and the health of our planet.
What's Your Reaction?
















