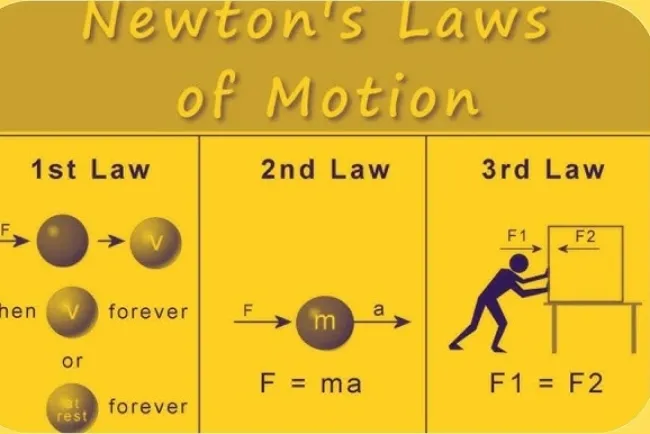
The Equator: A Line that Shapes Our Planet...!!!
The equator is an imaginary line encircling the Earth, situated equidistant from the North and South Poles, effectively dividing the planet into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. It is the longest line of latitude at 0 degrees and serves as a pivotal reference point for other lines of latitude. Spanning approximately 40,075 kilometers (24,901 miles), the equator passes through 13 countries, and its significance extends beyond mere geography, influencing climate, ecosystems, and human activities.
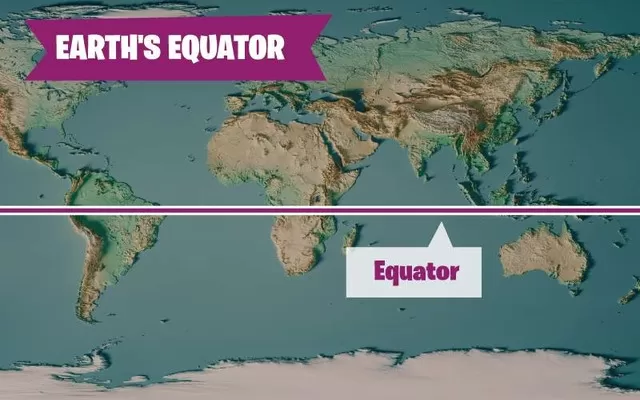
Geographical Significance
The equator holds a crucial geographical position as it lies midway between the poles and represents the intersection of the Earth's rotational axis with its surface. This axial tilt, combined with the equator's location, contributes to the phenomena of equinoxes—twice a year when day and night are of equal length globally. The equator also provides a foundational reference point for dividing the Earth into two equal halves, aiding in navigation and cartography.
Countries and Regions on the Equator
The equator traverses 13 countries: Ecuador, Colombia, Brazil, São Tomé and Príncipe, Gabon, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda, Kenya, Somalia, Indonesia, Kiribati, and the Maldives. These nations experience unique climatic conditions due to their proximity to the equator. For instance, in Ecuador, the equator is celebrated at "La Mitad del Mundo" (The Middle of the World), a well-known tourist attraction.
Climate and Weather Patterns
Regions along the equator are characterized by a tropical climate, with consistently high temperatures and significant rainfall throughout the year. This climate is attributed to the constant direct sunlight the equatorial region receives. Unlike temperate regions with marked seasonal temperature changes, equatorial areas experience minimal seasonal variation, typically having distinct wet and dry seasons instead.
Tropical Rainforests
One of the most remarkable features of the equatorial region is the presence of expansive tropical rainforests. These rainforests are biodiversity hotspots, home to an astounding variety of plant and animal species. The Amazon Rainforest in South America, the Congo Rainforest in Africa, and the rainforests of Southeast Asia are prime examples. These forests play a critical role in regulating the global climate by absorbing carbon dioxide and producing oxygen.

Ocean Currents and Marine Life
The equator also influences ocean currents, which in turn affect marine ecosystems and weather patterns. The Equatorial Currents, part of the larger oceanic conveyor belt, are instrumental in distributing heat across the planet. These currents impact marine life, supporting diverse ecosystems that include coral reefs, fish, and other marine organisms.
Human Settlements and Cultures
Human settlements near the equator have adapted to the region's unique climatic conditions. Traditional dwellings often feature designs that promote ventilation and cooling. Agriculture in equatorial areas typically focuses on crops that thrive in warm, humid conditions, such as bananas, coffee, and cocoa.
The equator also holds cultural significance in many societies. Indigenous communities in equatorial regions often have rich traditions and knowledge systems closely tied to their natural environments. Festivals, rituals, and practices related to the equator are common in these cultures.
Scientific Research and Exploration
The equator has been a focal point for scientific research and exploration. Due to the Earth's rotation, the equator experiences a phenomenon known as the Coriolis effect, which influences weather patterns and ocean currents. Studying this effect has provided valuable insights into atmospheric and oceanic dynamics.
Moreover, the equator's consistent climate makes it an ideal location for various scientific experiments. Observatories, research stations, and space agencies have set up facilities near the equator to take advantage of stable weather conditions. For example, the European Space Agency's Guiana Space Centre in French Guiana is located near the equator, allowing for efficient satellite launches.
The equator is much more than an imaginary line dividing the Earth into hemispheres. It plays a vital role in shaping the planet's climate, ecosystems, and human activities. From the tropical rainforests teeming with life to the scientific research that unravels the mysteries of our planet, the equator's influence is far-reaching and profound. Its unique position on Earth makes it a fascinating subject of study and a key element in understanding the interconnectedness of natural and human systems.
What's Your Reaction?