Medical Coding: Job Opportunities, Career Growth, and Types
Medical coding is a fast-growing career in the healthcare industry, offering job stability, competitive salaries, and various career advancement opportunities. With the increasing demand for accurate medical records and insurance processing, medical coders play a crucial role in healthcare documentation and billing.
Who Can Become a Medical Coder?
To become a medical coder, one needs:
- Training and Certification: Courses in medical coding are available online and in training institutes. Certifications like CPC (Certified Professional Coder) and CCS (Certified Coding Specialist) are widely recognized.
- Attention to Detail: Accuracy is essential to avoid billing errors.
- Knowledge of Medical Terminology: Understanding medical terms and anatomy helps in proper coding.
- There are two types of coders are present which is Certidied medical coder and Non-Certified medical coder.
For certification:
- To became a certified coder we have to take part in exam called CPC (CERTIFID PROFESSIONAL CODER) which can cost 750$.
Career Opportunities in Medical Coding
Medical coding offers various job roles across hospitals, clinics, insurance companies, and outsourcing firms. Some common job titles include:
1. Medical Coder
- Reviews patient records and assigns the correct codes for diagnoses and procedures.
- Works with ICD, CPT, and HCPCS coding systems.
2. Medical Billing and Coding Specialist
- Handles both coding and billing responsibilities.
- Ensures claims are submitted correctly to insurance companies.
3. Coding Auditor
- Reviews coded records for accuracy and compliance.
- Identifies errors and ensures proper claim processing.
4. Clinical Documentation Specialist
- Works with healthcare providers to improve medical record accuracy.
- Ensures documentation aligns with coding and billing regulations.
5. Medical Coding Trainer
- Trains new coders and keeps them updated with industry changes.
- Works in training institutes or hospitals.
6. Compliance Officer
- Ensures that coding and billing follow healthcare regulations.
- Helps organizations avoid fraud and billing errors.
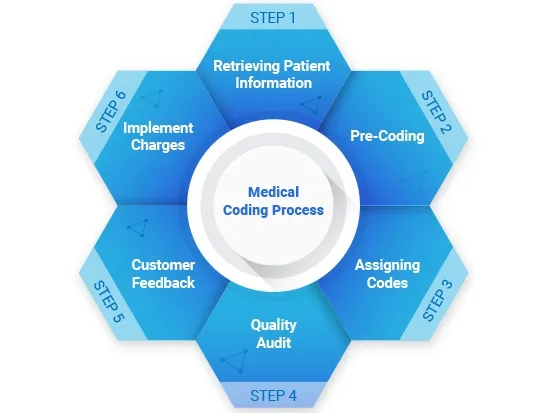
Career Growth and Salary Prospects
Medical coding offers excellent career growth opportunities. Entry-level coders can advance to senior roles with experience and certifications.
- Entry-Level Coders: Start as junior coders with basic coding tasks.
- Experienced Coders: With experience, coders can become auditors, trainers, or specialists in specific coding areas.
- Certified Coders: Certified professionals (e.g., CPC, CCS) earn higher salaries and have better job prospects.
Salary Expectations
Salaries vary based on experience, certification, and location:
- Entry-Level: $35,000 – $45,000 per year
- Mid-Level: $50,000 – $70,000 per year
- Senior-Level: $75,000+ per year
Certified coders tend to earn more than non-certified professionals.
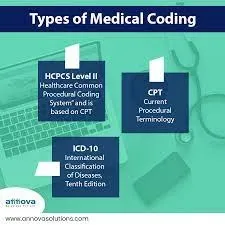
Types of Medical Coding
Medical coding is classified into different types based on its purpose and usage. The most common types include:
1. Diagnostic Coding
- Uses ICD (International Classification of Diseases) codes.
- Assigns codes for medical conditions and diagnoses.
- Example: E11.9 for type 2 diabetes mellitus without complications.
2. Procedural Coding
- Uses CPT (Current Procedural Terminology) codes.
- Codes medical procedures and treatments.
- Example: 99213 for a standard doctor’s visit.
3. Hospital Inpatient Coding
- Uses ICD-10-PCS (Procedure Coding System) for hospital treatments.
- Applied to surgeries and hospital-based procedures.
- Example: 0JH60MZ for knee replacement surgery.
4. Hospital Outpatient Coding
- Uses both CPT and ICD-10-CM for outpatient procedures.
- Applied to treatments that do not require hospitalization.
5. HCPCS Coding
- Uses HCPCS (Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System) codes.
- Covers medical equipment, supplies, and non-physician services.
- Example: E1130 for a wheelchair.
6. Radiology Coding
- Specific to medical imaging procedures like X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans.
- Uses CPT and ICD codes for accurate billing.
7. Pathology and Laboratory Coding
- Used for medical lab tests and diagnostic evaluations.
- Example: 80053 for a comprehensive metabolic panel.
Why Choose a Career in Medical Coding?
- High Demand: The healthcare industry is growing, increasing the need for coders.
- Work Flexibility: Many medical coding jobs offer remote work options.
- Career Advancement: With experience and certifications, coders can progress to higher positions.
- Competitive Salaries: Certified medical coders earn attractive salaries.
Conclusion
Medical coding is a promising career with numerous opportunities for growth. With the right training and certification, individuals can build a stable and rewarding career in healthcare documentation. Whether working in hospitals, insurance companies, or as a freelance coder, medical coding remains a vital part of the healthcare industry.







