Making of Glucose and Its Uses...!!!
Glucose is a vital molecule with a wide range of applications in biology, medicine, industry, and research. Its production through natural and industrial methods ensures a steady supply for various uses, highlighting its importance in sustaining life and advancing technology.
Glucose is a simple sugar and a vital carbohydrate in biology, serving as a primary energy source for living organisms and playing a key role in various metabolic processes.
Making of Glucose
-
Photosynthesis
-
Process: Photosynthesis is the natural method by which plants, algae, and some bacteria produce glucose. Using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water, these organisms synthesize glucose and release oxygen as a byproduct.
-
Equation: The chemical equation for photosynthesis is:
-
-
Chlorophyll: The green pigment chlorophyll in plant cells captures sunlight, driving the photosynthetic process.
-
Calvin Cycle: The Calvin cycle is a series of biochemical reactions occurring in the chloroplasts of plants, converting carbon dioxide and other compounds into glucose.
-
Industrial Production of Glucose
-
Starch Hydrolysis: Industrially, glucose is produced by hydrolyzing starch. Starch, derived from corn, potatoes, or other sources, is broken down into glucose using enzymes or acids.
-
Steps: The process involves gelatinization, liquefaction, and saccharification:
-
Gelatinization: Starch granules are heated in water, causing them to swell and form a gel.
-
Liquefaction: The gel is treated with enzymes like alpha-amylase, breaking down the starch into shorter chains called dextrins.
-
Saccharification: Another enzyme, glucoamylase, converts dextrins into glucose.
-
-
Purification: The resulting glucose solution is purified, concentrated, and crystallized for various uses.
-
-
Biotechnological Methods
-
Microbial Fermentation: Genetically modified microorganisms can produce glucose from renewable sources through fermentation.
-
Enzyme Engineering: Advances in enzyme engineering have led to more efficient enzymes for starch hydrolysis, improving glucose production yields.
-
Uses of Glucose
-
Biological Functions
-
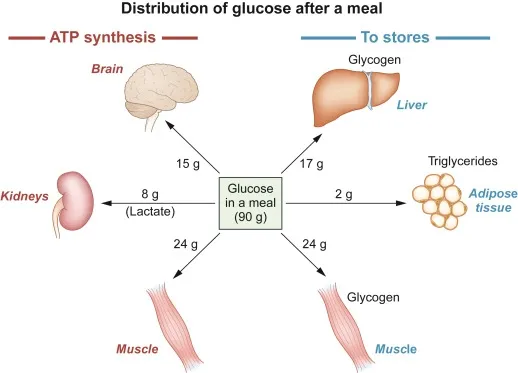
Energy Source: Glucose is the primary energy source for cells. It is metabolized through glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation to produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of the cell.
-
Brain Function: The brain relies on glucose as its main fuel source. Adequate glucose levels are essential for cognitive functions, including memory, learning, and concentration.
-
Glycogen Storage: Excess glucose is stored in the liver and muscles as glycogen, providing a readily available energy reserve during physical activity or fasting.
-
-
Medical Applications
-
Intravenous Solutions: Glucose solutions are used in intravenous (IV) therapy to provide energy and hydration to patients who cannot consume food orally. Common IV solutions include dextrose in water (D5W) and dextrose saline.
-
Hypoglycemia Treatment: Glucose tablets or gel are administered to individuals experiencing hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) to quickly raise blood glucose levels.
-
Diagnostic Tests: Glucose is used in medical diagnostic tests, such as the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), to assess glucose metabolism and diagnose conditions like diabetes.
-
-
Food and Beverage Industry
-
Sweetener: Glucose is used as a sweetener in various food and beverage products, enhancing the flavor and texture of items like candies, baked goods, and soft drinks.
-
Preservative: Glucose acts as a preservative by reducing water activity in foods, inhibiting the growth of microorganisms and extending shelf life.
-
Fermentation: Glucose is a key ingredient in fermentation processes for producing alcoholic beverages like beer and wine, as well as fermented foods like yogurt and sauerkraut.
-
-
Industrial Applications
-
Biofuels: Glucose is a feedstock for producing biofuels, such as ethanol. Microbial fermentation converts glucose into ethanol, which can be used as a renewable energy source.
-
Bioplastics: Glucose is used to produce biodegradable plastics through microbial fermentation. These bioplastics offer an eco-friendly alternative to conventional petroleum-based plastics.
-
Cosmetics: Glucose and its derivatives are used in cosmetics and personal care products for their moisturizing and stabilizing properties.
-
-
Research and Biotechnology
-
Cell Culture Media: Glucose is a critical component of cell culture media, providing energy for the growth and maintenance of cells in research and biotechnology applications.
-
Biotechnological Processes: Glucose is used as a carbon source in various biotechnological processes, including the production of enzymes, antibiotics, and other bio-products.
-
Glucose is a vital molecule with a wide range of applications in biology, medicine, industry, and research. Its production through natural and industrial methods ensures a steady supply for various uses, highlighting its importance in sustaining life and advancing technology.
What's Your Reaction?

















