Hypergraph Diffusion for High-Order Recommender Systems
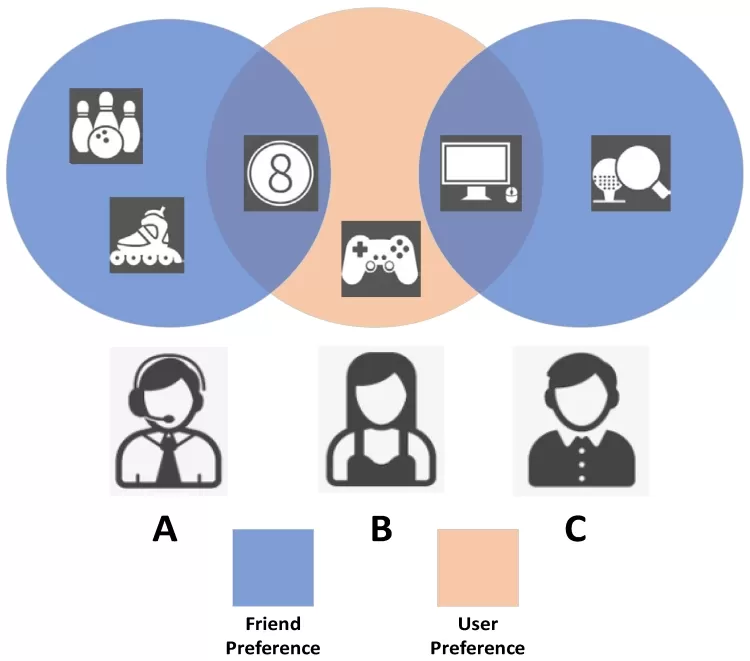
Recommender systems have become an essential tool in diverse applications like e-commerce, entertainment, and social networks. They rely heavily on Collaborative Filtering (CF) to predict a user's preference based on historical interactions with items. While traditional CF methods focus on vector embeddings of users and items, graph-based methods, especially Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), have proven to be more effective by leveraging the rich topological structures of user-item interaction graphs.
Despite this, existing GNN-based models such as LightGCN and UltraGCN still face two major challenges: heterophilic interactions, where users engage with items across different categories, and the over-smoothing problem in multi-layer GNNs, which affects the modeling of complex, high-order relationships. In this paper, we introduce WaveHDNN, a wavelet-enhanced hypergraph diffusion framework, designed to address these limitations by combining a Heterophily-aware Collaborative Encoder and a Multi-scale Group-wise Structure Encoder. This approach significantly improves recommendation accuracy by capturing both heterophilic patterns and localized structural information.
Introduction to Collaborative Filtering and Graph-based Approaches
Collaborative Filtering (CF) is widely used in recommender systems to predict user preferences based on their interaction history. Traditional CF methods like Matrix Factorization (MF) and Neural Collaborative Filtering (NCF) focus on learning low-dimensional embeddings for users and items, capturing their interactions through latent factors. While these methods have demonstrated effectiveness, they often struggle with scalability and data sparsity in large datasets.
Graph-based Collaborative Filtering (GCF) methods, on the other hand, leverage the relationships between users and items represented as a graph. Methods like NGCF (Neural Graph Collaborative Filtering) and LightGCN use Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) to capture user-item interactions. These models improve the expressiveness of embeddings by directly modeling graph-based relationships. However, they still struggle to capture more complex relationships, particularly heterophilic interactions where users engage with items from diverse categories.
The Need for Heterophilic Interaction Modeling
In many real-world scenarios, a user may interact with a wide variety of items across different categories. For example, a user might enjoy movies, books, and music from completely different genres. Heterophilic interactions are not well represented by traditional GCN models, which primarily assume that similar users interact with similar items. This leads to challenges in accurate recommendation when a user's interactions span multiple categories.
The Over-Smoothing Problem
Another limitation of existing GNN-based models is the over-smoothing problem in multi-layer GCNs. As the number of layers increases, the learned representations of nodes (users and items) become too similar, leading to poor performance in capturing complex relationships. This is especially problematic in recommendation systems, where capturing the diversity and nuances of user-item interactions is crucial.
WaveHDNN: A Novel Approach to High-Order Recommender Systems
To address these challenges, we propose WaveHDNN, an innovative framework that integrates a Heterophily-aware Collaborative Encoder and a Multi-scale Group-wise Structure Encoder.
Heterophily-aware Collaborative Encoder
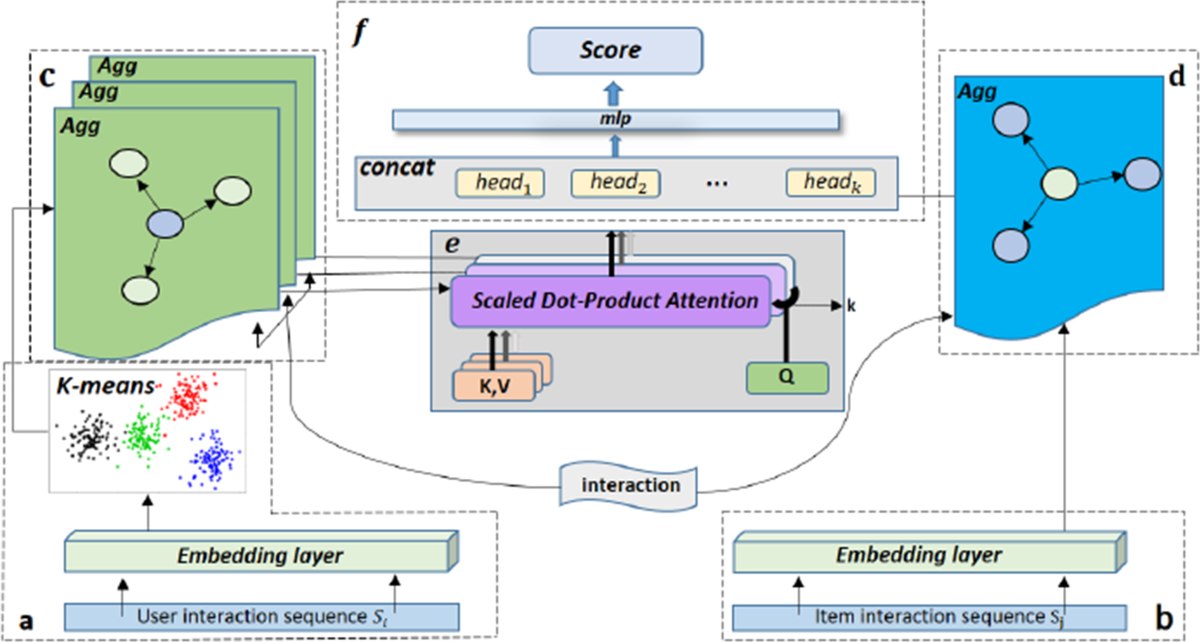
The Heterophily-aware Collaborative Encoder is designed to account for heterophilic patterns in user-item interactions. It employs an equivariant operator inspired by ED-HNN to differentiate messages passed to heterogeneous nodes. This allows the model to distinguish between interactions involving similar and diverse item categories, improving its ability to handle heterophilic relationships effectively.
Multi-scale Group-wise Structure Encoder
The Multi-scale Group-wise Structure Encoder leverages wavelet transforms combined with hypergraph convolutional layers to capture localized structural information. The wavelet transform allows the model to adaptively adjust the spread of information across the hypergraph, capturing relationships at multiple scales and improving the model’s ability to handle complex dependencies between users and items.
Cross-view Contrastive Learning
To ensure that the two encoders provide consistent representations, we introduce cross-view contrastive learning. This technique aligns the embeddings of the same entities across the two encoders, ensuring that both local and global relationships are consistently represented in the learned embeddings.
Experimental Validation
We evaluate WaveHDNN on several benchmark datasets, comparing it to state-of-the-art models like LightGCN and UltraGCN. The results demonstrate that WaveHDNN outperforms these models by capturing both heterophilic patterns and localized topological information, leading to improved recommendation accuracy.
Conclusion
In this work, we present WaveHDNN, a wavelet-based hypergraph diffusion model designed to address two key challenges in graph-based recommender systems: heterophilic interactions and over-smoothing in multi-layer GCNs. By combining a Heterophily-aware Collaborative Encoder with a Multi-scale Group-wise Structure Encoder, WaveHDNN effectively models both global and local dependencies in user-item interactions. Our experimental results validate the efficacy of the proposed model, showing significant improvements over existing methods.
This work highlights the importance of incorporating both heterophilic interaction modeling and localized structural learning in graph-based recommender systems, offering a promising direction for future research in high-order recommendation models.
What's Your Reaction?

















