Detailed Overview of the India Map...!!!
The map of India is a multifaceted tool that provides valuable insights into the country’s geography, political boundaries, cultural regions, and economic activities.
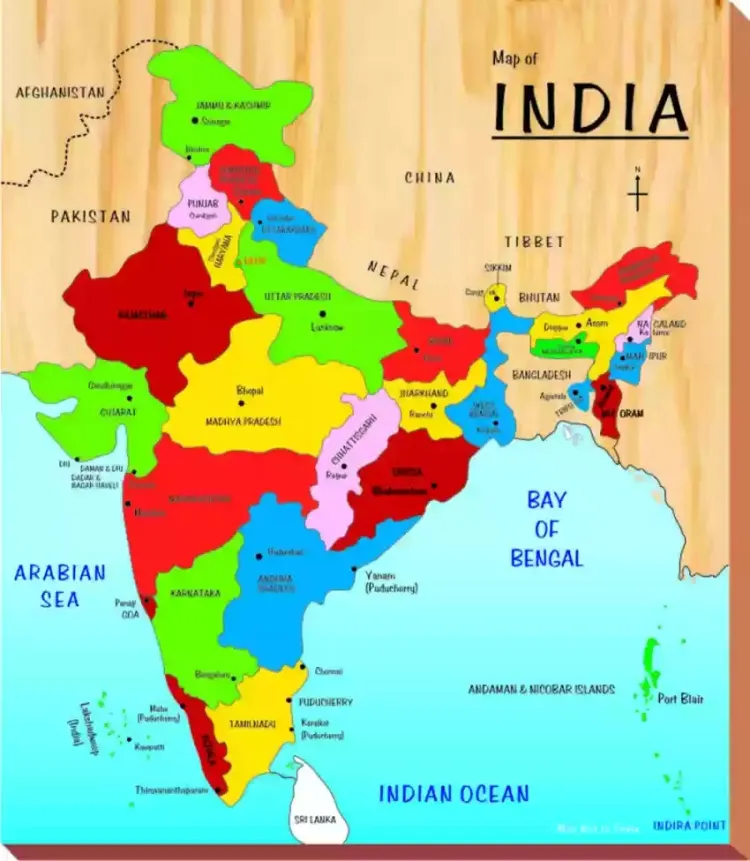
Introduction
India, a vast and diverse country located in South Asia, is the seventh-largest by land area and the second-most populous in the world. The map of India is a crucial tool for understanding its geographical features, political boundaries, cultural regions, and economic activities. Here's a detailed exploration of India's map, its key features, and its uses.
Geographical Features
-
Physical Geography
-
Mountain Ranges: The northern part of India is dominated by the Himalayan mountain range, home to some of the world's highest peaks, including Mount Everest (shared with Nepal) and Kanchenjunga. The Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats run parallel to the western and eastern coasts, respectively, influencing the region's climate and biodiversity.
-
Plains: The Indo-Gangetic Plain, formed by the Ganges, Indus, and Brahmaputra river systems, is one of the most fertile and densely populated regions globally. This plain stretches across northern and eastern India.
-
Deserts: The Thar Desert, also known as the Great Indian Desert, is situated in the northwestern part of India, primarily in Rajasthan.
-
Plateaus: The Deccan Plateau, covering much of southern India, is a vast, elevated area that includes several rivers and hill ranges.
-
Coastal Areas: India boasts a long coastline of about 7,500 kilometers, with the Arabian Sea to the west, the Bay of Bengal to the east, and the Indian Ocean to the south.
-
-
Rivers and Water Bodies
-
Major Rivers: India’s major rivers include the Ganges, Yamuna, Brahmaputra, Godavari, Krishna, and Narmada. These rivers are vital for agriculture, transportation, and cultural practices.
-
Lakes: Prominent lakes like Vembanad Lake in Kerala, Chilika Lake in Odisha, and Dal Lake in Jammu and Kashmir play important roles in biodiversity, tourism, and local economies.
-

Political Boundaries
-
States and Union Territories
-
States: India is divided into 28 states, each with its government and administrative structures. Some of the largest states by area include Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and Maharashtra. Uttar Pradesh is the most populous state.
-
Union Territories: There are 8 Union Territories, which are regions governed directly by the Central Government. Examples include Delhi, Puducherry, and Chandigarh.
-
-
International Borders
-
Neighboring Countries: India shares its borders with Pakistan to the northwest, China to the north, Nepal and Bhutan to the northeast, Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east, and Sri Lanka to the south (maritime boundary).
-
Cultural Regions
-
Languages
-
India is home to a diverse range of languages, with 22 officially recognized languages, including Hindi, Bengali, Telugu, Marathi, Tamil, and Urdu. Each state often has its dominant language and cultural identity.
-
-
Religions
-
India is a land of religious diversity, with major religions including Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, Sikhism, Buddhism, and Jainism. Each religion has its cultural and historical significance, contributing to the country's rich heritage.
-
-
Festivals and Traditions
-
Festivals like Diwali, Holi, Eid, Christmas, and Pongal are celebrated across different regions with unique customs and traditions, reflecting India's cultural diversity.
-
Economic Activities
-
Agriculture
-
The Indo-Gangetic Plain and other fertile regions support extensive agricultural activities, including the cultivation of rice, wheat, sugarcane, and cotton.
-
-
Industry
-
Industrial regions are spread across the country, with major hubs in states like Maharashtra, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, and Karnataka. Key industries include information technology, manufacturing, textiles, and automotive production.
-
-
Tourism
-
India's diverse landscapes, cultural heritage, and historical landmarks attract tourists from around the world. Popular destinations include the Taj Mahal, Jaipur, Kerala’s backwaters, and Goa’s beaches.
-
Modern Uses of India's Map
-
Education
-
Maps are essential tools in classrooms for teaching students about India’s geography, states, capitals, and cultural diversity.
-
-
Planning and Development
-
Government agencies and planners use maps for urban planning, infrastructure development, resource management, and environmental conservation.
-
-
Navigation and Travel
-
Maps assist travelers and navigators in planning routes, exploring destinations, and understanding distances between places.
-
The map of India is a multifaceted tool that provides valuable insights into the country’s geography, political boundaries, cultural regions, and economic activities. It plays a crucial role in education, planning, navigation, and understanding India’s diverse and dynamic nature. Whether for academic purposes, travel planning, or policy-making, the map of India remains an indispensable resource.
What's Your Reaction?